Push Notification
Push notifications are one of the most effective ways to communicate with your subscribers. They reach devices directly—even when your app isn’t open—making them the perfect channel for important alerts, urgent reminders, and updates that require immediate attention.
What Is the Push Notification Node?
The Push Notification Node sends push notifications to your subscribers’ devices as part of your workflows. These notifications appear in the device’s notification tray, whether on a mobile phone, tablet, or web browser.
Unlike emails that can sit unread in an inbox, push notifications are immediate and highly visible. They’re ideal for communications that require fast action or that you want subscribers to see right away.
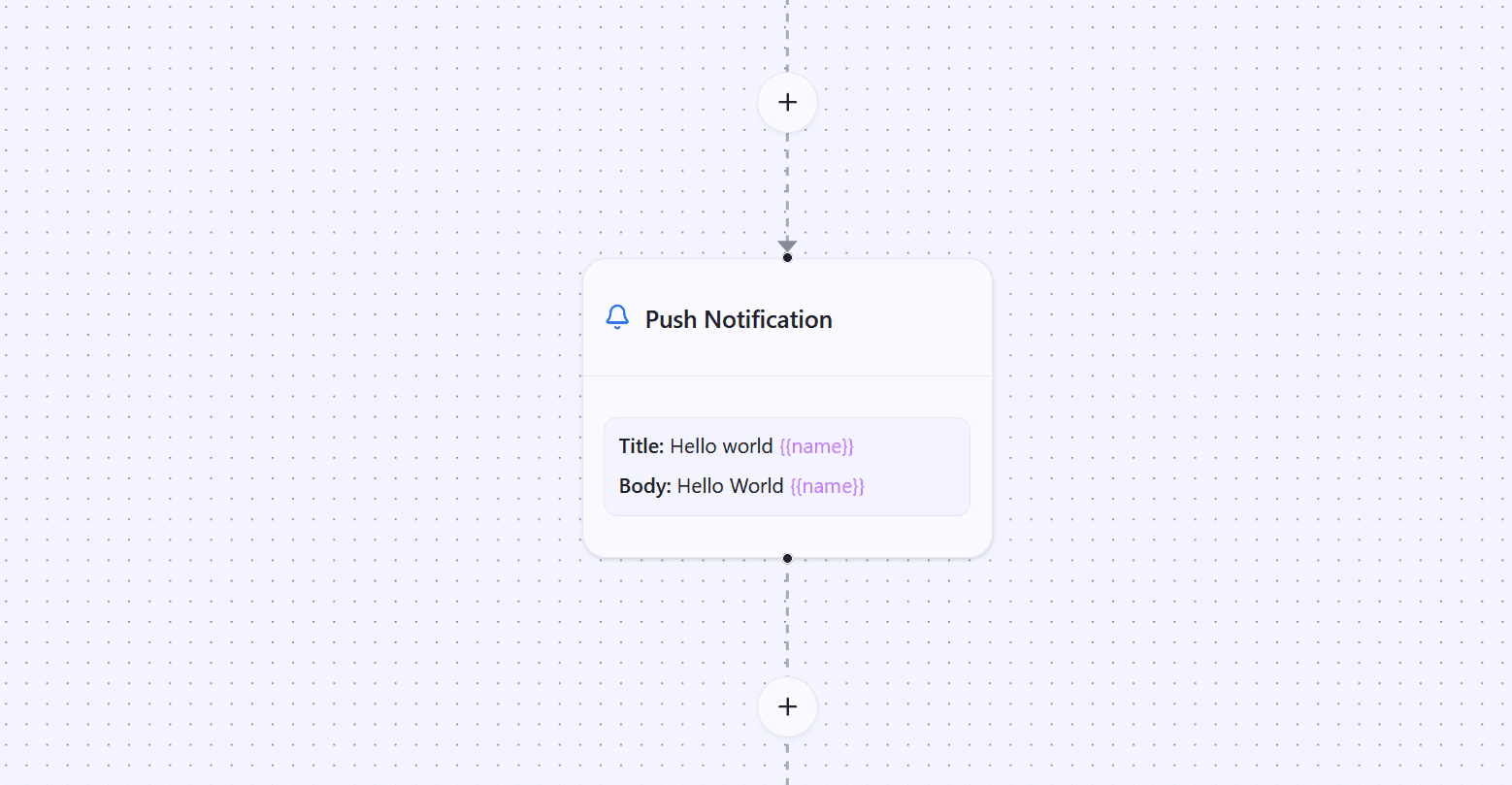
How Push Notifications Work
When you configure a Push Notification Node, you define a title and a message body. These are shown in the notification received by the subscriber. Both can be personalized using dynamic parameters that are replaced with subscriber-specific data.
Notifications are delivered through Firebase Cloud Messaging (FCM), the industry-standard platform for push notifications. This ensures reliable delivery across platforms.
Supported Platforms
All Platforms
The most common option is sending to all platforms at once. This maximizes reach and keeps configuration simple. When selected, PushFire sends the notification to all registered subscriber devices, whether Android, iOS, or Web.
Web
Web notifications use the Browser Notifications API and require the subscriber to grant notification permissions. Once enabled, notifications can appear even when the subcriber isn’t actively browsing your site.
They’re especially useful for Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) and websites that want to keep subscribers informed without requiring constant visits.
Android
Android notifications are delivered via Firebase Cloud Messaging and appear natively in the system notification tray. They integrate seamlessly with the Android subscriber experience.
Your Android app must be configured with FCM, and subscribers must grant notification permissions.
iOS
iOS notifications also use Firebase Cloud Messaging but are delivered through Apple Push Notification Service (APNs). They require APNs certificates configured in Firebase and subscriber permission.
They integrate with iOS-native features such as Focus Modes and Notification Summary.
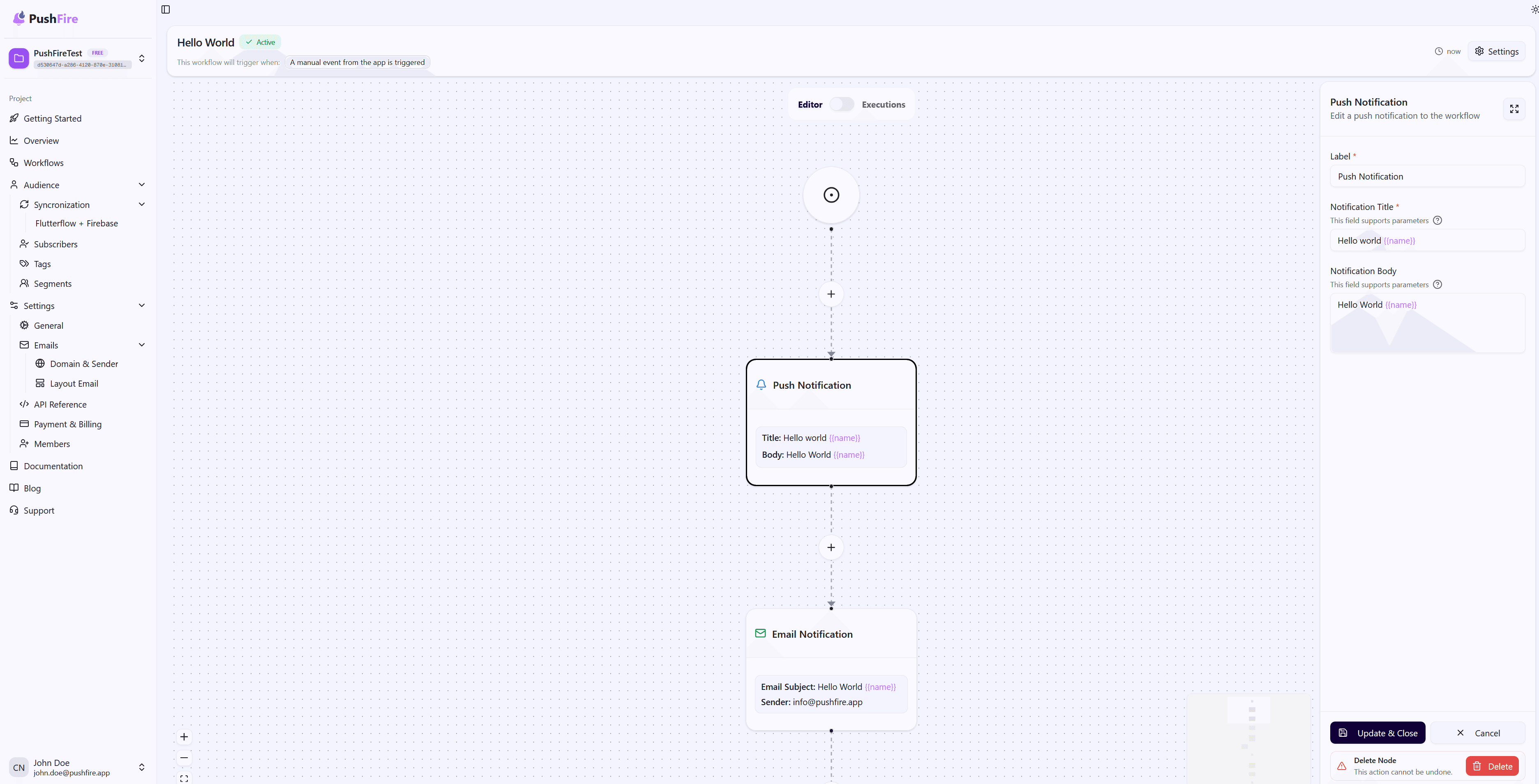
Configuring Your Push Notification Node
Notification Title
The title is the first thing subscribers see. It should be short, clear, and attention-grabbing. Long titles are truncated, so keep them concise.
You can use dynamic parameters to personalize the title. For example,
“Hi {{name}}! You have a new update” becomes “Hi Juan! You have a new update.”
Notification Body
The body provides additional context. While optional, it’s strongly recommended. A good body explains why the subscriber is receiving the notification and what action they can take.
Dynamic parameters can also be used here, making notifications feel personal and relevant.
Available Dynamic Parameters
You can use the following parameters in titles and bodies:
{{name}}: Subscriber’s name.
{{email}}: Subscriber’s email address.
{{phone}}: Subscriber’s phone number.
{{metadata.key}}: Any custom value from subscriber metadata, for example {{metadata.unread_count}}.
Common Use Cases
Immediate Alerts
Perfect for alerts that need instant attention, such as payment confirmations, status changes, or actions requiring confirmation.
Reminders
Send reminders for pending tasks, upcoming appointments, or actions the subscriber needs to complete. Push notifications are more visible than emails, making them ideal for reminders.
Content Updates
Notify subscribers when new content is available—new articles, app updates, or personalized content based on interests.
Re-engagement
Bring inactive subscribers back with well-crafted push notifications that spark interest and action.
Best Practices
Keep Messages Concise
Notification space is limited. Aim for titles under 50–60 characters and bodies that are brief but informative.
Use Dynamic Parameters
Personalization boosts engagement. Dynamic parameters make notifications feel relevant and tailored.
Consider Timing
Avoid overwhelming subscribers. Use Wait Nodes to space notifications and consider time zones when possible.
Deliver Real Value
Every notification should benefit the subscriber—important information, a required action, or meaningful content.
Test Across Platforms
Notifications look different on Android, iOS, and Web. Always test on all platforms to ensure consistent quality.
Troubleshooting
If notifications aren’t sent, check that devices are properly registered in PushFire with valid FCM tokens and notifications enabled.
If dynamic parameters don’t render correctly, verify the syntax. Parameters must use double curly braces, like {{name}}, and the subscriber must have that field defined.
If notifications only arrive on some platforms, ensure all devices are registered correctly and that Firebase Cloud Messaging is properly configured for each platform.